Ch 12. 딥러닝 입문 (분류)
Part.7 Deep Classification 실습
Classification with Deep Neural Networks
Load MNIST Dataset: 손글씨 글자 Classification
- In [1] :
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
- In [2] :
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
- In [3] :
- 여기서 만약 MNIST dataset가 없으면 자동으로 다운로드 하고, MNIST dataset가있으면 그냥 있는거 쓴다.
train = datasets.MNIST(
'../data', train=True, download=True, # MNIST 없을때 자동으로 DOWNLOAD
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
]),
)
test = datasets.MNIST(
'../data', train=False, # 있을경우엔 있는거 쓴다
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
]),
)
- In [4] :
def plot(x):
img = (np.array(x.detach().cpu(), dtype='float')).reshape(28,28)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
- In [5] :
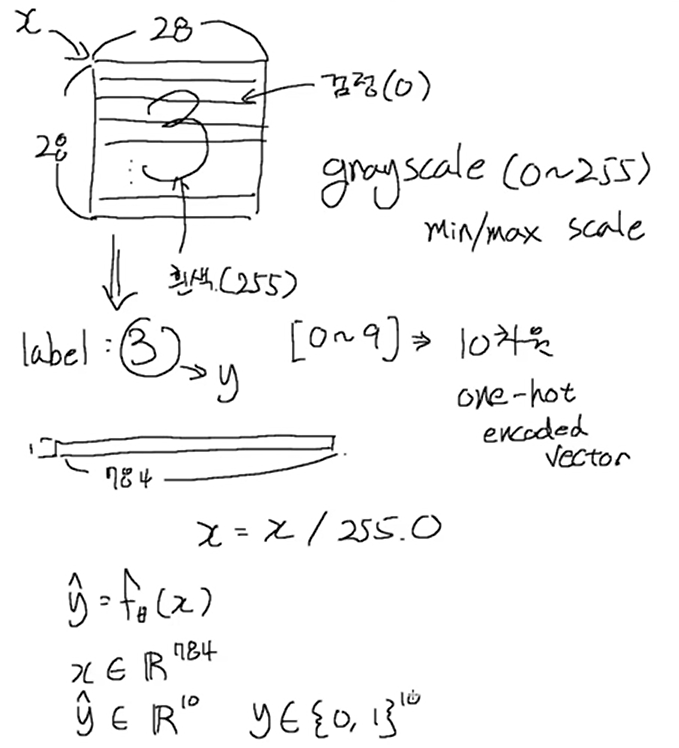
- 글자는 gray scale(0~255)로 되어있다. 28x28 (size)
-
글씨를 보고 어떤 글씨인지 맞춰야 한다. 5 -> y
- 이미지를 벡터화 (784차원의 vector)
- y[0~9]: 10차원 one-hot encoded vector
plot(train.data[0])
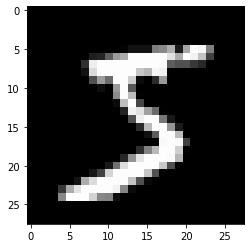
- In [6] :
x = train.data.float() / 255.
y = train.targets
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
print(x.shape, y.shape)
input_size = x.size(-1)
output_size = int(max(y)) + 1
print('input_size: %d, output_size: %d' % (input_size, output_size))
torch.Size([60000, 784]) torch.Size([60000])
input_size: 784, output_size: 10
- In [7] :
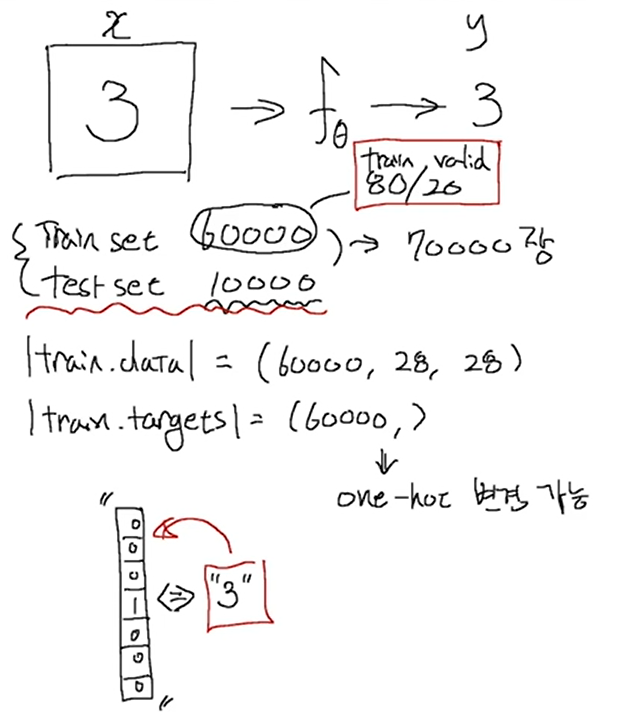
# Train / Valid ratio
ratios = [.8, .2]
train_cnt = int(x.size(0) * ratios[0])
valid_cnt = int(x.size(0) * ratios[1])
test_cnt = len(test.data)
cnts = [train_cnt, valid_cnt]
print("Train %d / Valid %d / Test %d samples." % (train_cnt, valid_cnt, test_cnt))
indices = torch.randperm(x.size(0))
x = torch.index_select(x, dim=0, index=indices)
y = torch.index_select(y, dim=0, index=indices)
x = list(x.split(cnts, dim=0))
y = list(y.split(cnts, dim=0))
x += [(test.data.float() / 255.).view(test_cnt, -1)]
y += [test.targets]
for x_i, y_i in zip(x, y):
print(x_i.size(), y_i.size())
#여기서 Y는 INDEX의 벡터가 아니라 Long Tensor 이다.
Train 48000 / Valid 12000 / Test 10000 samples.
torch.Size([48000, 784]) torch.Size([48000])
torch.Size([12000, 784]) torch.Size([12000])
torch.Size([10000, 784]) torch.Size([10000])
Build Model & Optimizer
- In [8] :
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_size, 500),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(500, 400),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(400, 300),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(300, 200),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(200, 100),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(100, 50),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(50, output_size),
nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1),
)
model
- Out [8] :

Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=500, bias=True)
(1): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01)
(2): Linear(in_features=500, out_features=400, bias=True)
(3): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01)
(4): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=300, bias=True)
(5): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01)
(6): Linear(in_features=300, out_features=200, bias=True)
(7): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01)
(8): Linear(in_features=200, out_features=100, bias=True)
(9): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01)
(10): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=50, bias=True)
(11): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01)
(12): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10, bias=True)
(13): LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
)
- In [9] :
crit = nn.NLLLoss()
- In [10] :
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())
Move to GPU if it is available
- In [11] :
device = torch.device('cpu')
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device('cuda')
- In [12] :
model = model.to(device)
x = [x_i.to(device) for x_i in x]
y = [y_i.to(device) for y_i in y]
Train
- In [13] :
n_epochs = 1000
batch_size = 256
print_interval = 10
- In [14] :
from copy import deepcopy
lowest_loss = np.inf
best_model = None
early_stop = 50
lowest_epoch = np.inf
- In [15] :
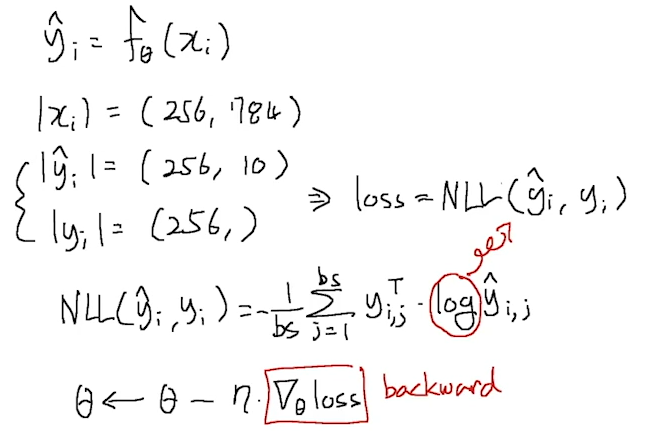
rain_history, valid_history = [], []
for i in range(n_epochs):
indices = torch.randperm(x[0].size(0)).to(device)
x_ = torch.index_select(x[0], dim=0, index=indices)
y_ = torch.index_select(y[0], dim=0, index=indices)
x_ = x_.split(batch_size, dim=0)
y_ = y_.split(batch_size, dim=0)
train_loss, valid_loss = 0, 0
y_hat = []
for x_i, y_i in zip(x_, y_):
y_hat_i = model(x_i)
loss = crit(y_hat_i, y_i.squeeze())
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_loss += float(loss) # This is very important to prevent memory leak.
train_loss = train_loss / len(x_)
with torch.no_grad():
x_ = x[1].split(batch_size, dim=0)
y_ = y[1].split(batch_size, dim=0)
valid_loss = 0
for x_i, y_i in zip(x_, y_):
y_hat_i = model(x_i)
loss = crit(y_hat_i, y_i.squeeze())
valid_loss += float(loss)
y_hat += [y_hat_i]
valid_loss = valid_loss / len(x_)
train_history += [train_loss]
valid_history += [valid_loss]
if (i + 1) % print_interval == 0:
print('Epoch %d: train loss=%.4e valid_loss=%.4e lowest_loss=%.4e' % (
i + 1,
train_loss,
valid_loss,
lowest_loss,
))
if valid_loss <= lowest_loss:
lowest_loss = valid_loss
lowest_epoch = i
best_model = deepcopy(model.state_dict())
else:
if early_stop > 0 and lowest_epoch + early_stop < i + 1:
print("There is no improvement during last %d epochs." % early_stop)
break
print("The best validation loss from epoch %d: %.4e" % (lowest_epoch + 1, lowest_loss))
model.load_state_dict(best_model)
Epoch 10: train loss=2.2119e-02 valid_loss=1.1302e-01 lowest_loss=9.5662e-02
Epoch 20: train loss=1.1494e-02 valid_loss=1.1124e-01 lowest_loss=9.5662e-02
Epoch 30: train loss=7.9660e-03 valid_loss=1.1719e-01 lowest_loss=9.5662e-02
Epoch 40: train loss=4.3731e-03 valid_loss=1.2816e-01 lowest_loss=9.5662e-02
Epoch 50: train loss=4.4661e-03 valid_loss=1.3524e-01 lowest_loss=9.5662e-02
There is no improvement during last 50 epochs.
The best validation loss from epoch 8: 9.5662e-02
- Out [15] :